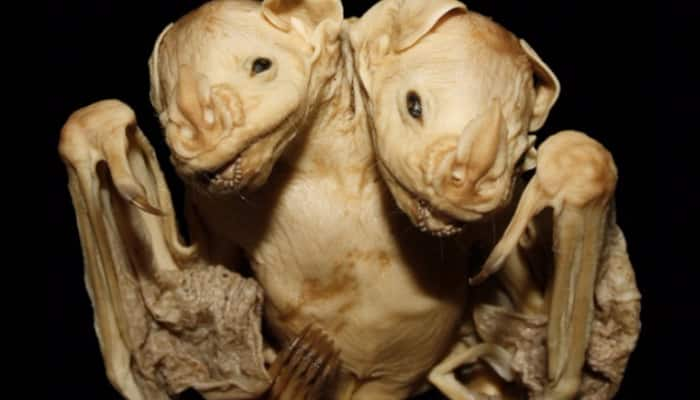
New Delhi: Scientists have been left baffled after discovering a corpse of rare conjoined bats in southeastern Brazil. It is believed to be the third case recorded and experts are now examining their remains to find out more about it.
The bats were initially found under a mango tree in the country in 2001 and are believed to have been stillborn and still had the placenta attached when discovered.
According to a report in the Daily Mail, the newborn bat twins' corpse is conjoined at the torso, with its two heads side by side.
As per reports, the twins have separated heads and necks but a conjoined trunk with an abnormally expanded thorax, with ultrasound analysis revealing that they have two similarly sized, separate hearts
Although it is unknown what causes identical twins to be conjoined, it is said that the phenomenon can occur when a fertilized egg splits too late.
Researchers came to know about the rare conjoined bats after the animals were donated to the Laboratory of Mastozoology at the Rural Federal University of Rio de Janeiro.
Reportedly, the study, led by a researcher based at the State University of Northern Rio de Janeiro, found that the bat twins were male large fruit-eating bats of the genus Artibeus.
The only other two cases of conjoined bats were reported in 1969 and 2015.